In India, the Fintech industry has been booming, and it’s expected to be worth $150 billion by 2025, growing at a rate of 22% per year2. As a result of this growth and wider impact on financial services, Fintechs are drawing the attention of regulators and policymakers.
The research paper on the Impact of Fintech Firms on Bank Financial Stability in the Journal Electronic Commerce Research (2022) discusses how the growth of Fintech companies, which use technology to provide financial services, impacts the stability of traditional banks. The sample consists of 26 Islamic and conventional banks from Malaysia from 2003 to 20181. It was found that FinTech companies came into existence because traditional banks had problems, especially during the global financial crisis in 2007-2008. Fintech stepped in to offer solutions to these problems.
Fintech companies offer cheaper and more efficient services, impacting traditional banks’ loan profits. To stay strong, banks should invest in innovation. Banks can respond to Fintech competition by incorporating Fintech services to enhance efficiency and stability or taking risks to maintain profits. Smaller banks adapt faster due to their size and flexibility, while larger banks should protect their customer base with competitive services. Banks with weak corporate governance may be more inclined to adopt Fintech services to address governance issues.
India Perspective
In India, large banks are actively integrating with fintech companies. The future of India’s financial sector depends on these partnerships, combining traditional banking strengths with fintech innovation. We expect more such collaborations in the coming years thereby, playing a crucial role in India’s $5 trillion economy goal4.
Figure 1: Partnership between Banks and Fintechs
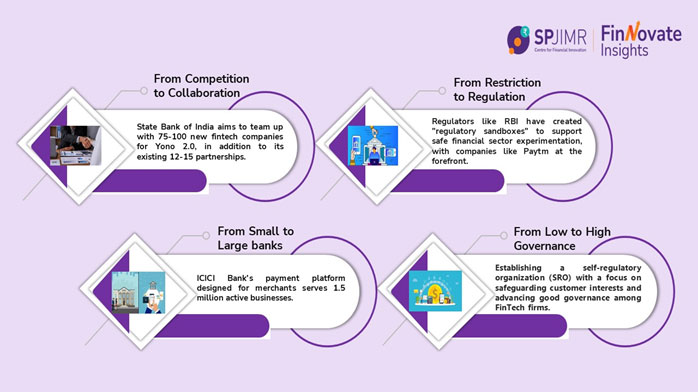
Rise of Fintechs
The rising trajectory of Fintech companies in banks seems to improve the system’s financial soundness. A recent report by CRISIL Research highlighted the various aspects that have impacted Fintech firms3.
1. Expanding Market Size
Owing to the rise of Fintechs, private banks, and brokerage players have been quick to adapt to changes. But smaller and mid-sized public sector banks have been lagging. The reason can be high initial investments and smaller customer bases which lead to slower adoption rates. Small banks have started embracing neobank architecture. This approach enables them to operate at a lower cost while maintaining compliance. But overall Fintech has pushed the traditional players to relook at their growth strategies positively.
2. Enhancing operational efficiency
Fintechs have been at the forefront of automation. Today, automation has become a crucial factor in the success of brokerage players and large private banks. Smaller NBFCs and PSUs are however lagging in embracing automation. The reason may be their risk-averse nature or scale of operations. They should consider automated solutions to streamline their loan processing workflow and improve their ability to bear risks. With advancements in technology like artificial intelligence and robotics, the initial investment in automation may seem daunting, but the long-term benefits are undeniable. The potential reduction in costs and improved efficiency will serve as a competitive advantage for smaller banks in the financial market.
3. Offering new products
The use of technology in cross-selling has become crucial for large private banks to manage and expand their product offerings. With data mining at their disposal, these banks can target existing customers and offer them personalized products such as personal loans. Small and mid-sized NBFCs and PSUs lag in this aspect due to a limited customer base and changing market demands. These banks need to take a proactive approach to increasing their product portfolio to stay competitive and ensure financial stability. By leveraging technology and data analytics, smaller banks can also tap into the potential of cross-selling and provide their customers with a wider range of services.
4. Customer service and engagement
Fintechs upended the conventional wisdom that you need a large branch presence to drive customer satisfaction. Larger new private banks have harnessed the power of digital channels to improve customer engagement and query resolution. With the implementation of AI bots and automated processes, these banks have not only enhanced efficiency but also instilled a sense of security in their customers. Small and mid-sized NBFCs and PSUs who have been lagging on this front, need to consider this an opportunity to offer personalized and relevant products.
5. Reach more unserved and underserved customers
The collaboration between large private banks and digital solution providers has led to innovative solutions for semi-urban and rural sectors. However, there is still room for growth in reaching out to more customers, especially in the small and mid-sized PSU segment. To bridge this gap, small banks must focus on expanding their reach and offerings, while also keeping up with the advancements made by fintech competitors. These banks need to evolve from focusing on payments and branching into core areas like savings and credit. With such efforts, we can expect to see increased financial stability and improved access to financial services for all segments of society.
6. Lowered Cost for unserved and underserved customers
On this front, surprisingly large new private banks are lagging in responsiveness to fintech. The brokerage players of small and & mid-sized NBFCs, and even large PSUs are more responsive towards an accelerated focus on fintechs to serve the unserved market. Large new private banks may still prioritize established markets to maintain profit margins.
Figure 2: Impact of Fintech
On a scale of 1 to 10 where 1 = Lowest adoption and 10 = Highest adoption
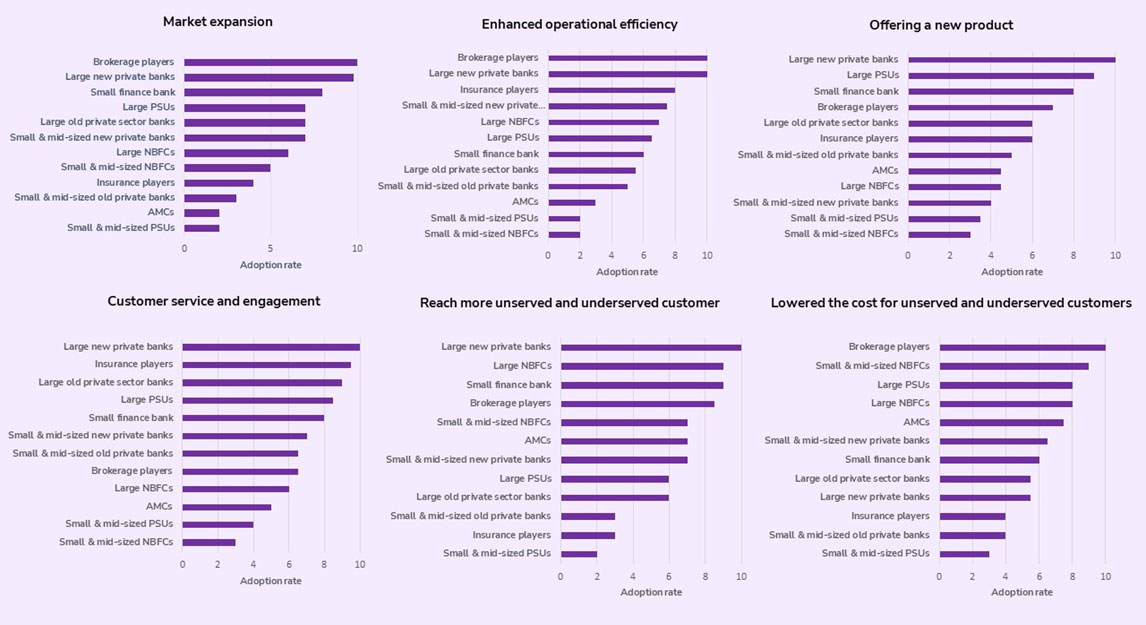
Source: CRISIL research
Conclusion
Overall, the growth of Fintechs has been hugely positive for India; with Fintechs providing higher accessibility and affordability of financial services. Traditional banks will need to adapt to these changes by incorporating Fintech services. Smaller banks are often quicker to adapt, and banks with low corporate governance may rely more on Fintechs to address their governance issues. With the right balance between innovation and customer protection, the industry has the potential to grow even further.
Sources:
1. Safiullah, M., Paramati, S.R., Impact of Fintech firms on bank financial stability. Electronic Commerce Research (2022).
2. The Economic Times
3. https://issuu.com/humanxdesign/docs/impact_of_digital_transformation_on_incumbents_ful
4. livemint.com